AutoFS: AutoFS is a file system mechanism that provides automatic mounting the NFS protocol. It is a client side service. AutoFS service mounts and unmounts file systems as required without any user intervention. Autofs is a program that automatically mounts specified directories on an on-demand basis. It is based on a kernel module for high efficiency, and can manage both local directories and network shares. These automatic mount points are mounted only when they are accessed, and unmounted after a certain period of inactivity. This on-demand behavior saves bandwidth and results in better performance.
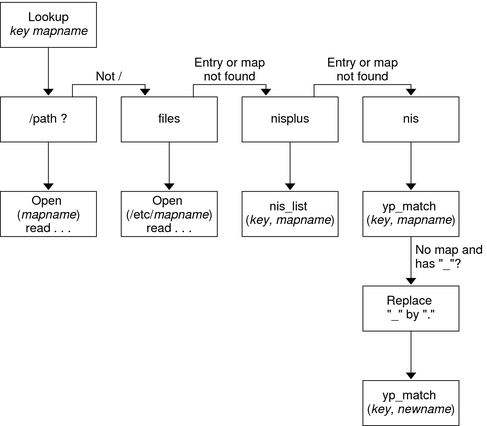
autofs provide a mechanism to automatically mount file systems at arbitrary points in the file system hierarchy. A direct map is denoted by a mount point of /- in the master map. Entries in a direct map contain an absolute path name as a key (instead of the relative path names used in indirect maps). -hosts map, commonly used for automounting all exports from a host under '/net/host' as a multi-mount map entry. When using the '-hosts' map, an 'ls' of '/net/host' will mount autofs trigger mounts for each export from host and mount and expire them as they are accessed. This can greatly reduce the number of active mounts needed when accessing a server with a large number of exports. autofs version 5 has been enhanced in several ways with respect to autofs version 4. The autofs configuration file (/etc/sysconfig/autofs) provides a mechanism to specify the autofs schema that a site implements, thus precluding the need to determine this via trial and error in the application itself. In addition, authenticated binds to the LDAP server are now supported, using most mechanisms supported by the common LDAP server implementations. A new configuration file has been added for this support: /etc/autofs_ldap_auth.conf. The default configuration file is self-documenting, and uses an XML format. nsswitch) configuration.man nsswitch.conf for more information on the supported syntax of this file. Please note that not all NSS databases are valid map sources and the parser will reject ones that are invalid. Valid sources are files, yp, nis, nisplus, ldap, and hesiod. /-. The map keys for each entry are merged and behave as one map. What is Autofs?
Why should I use Autofs ?
Advantages of AutoFS
- Shares are accessed automatically and transparently when a user tries to access any files or directories under the designated mount point of the remote filesystem to be mounted.
- Booting time is significantly reduced because no mounting is done at boot time.
- Network access and efficiency are improved by reducing the number of permanently active mount points.
- Failed mount requests can be reduced by designating alternate servers as the source of a filesystem.
In this article I will show you the configuration steps for autofs using NFS share
We we have two servers namely nfsserver and nfsclient. Lets start configuring a NFS share on nfsserver Divx pro 10 4 download free.
On nfsserver
Restart the nfs services or reload the shares
NOTE: Do not run this command on production environment if anyone is accessing any of the share as it will disrupt the traffic for few seconds.
Genreally we reload the nfs share using the below command
To see all the shares and the applied permissions
Well our server side work is done lets roll over to nfsclient
NOTE: For this article I have disabled my iptables and selinux.
In case you want to use iptables insert the below rule into your INPUT chain
On nfsclient
This is the place where the magic will happen. But for that we will have to configure autofs.
auto.master file
mount-point map-name options
For our case
Description
Description |
The autofs mount point, /mnt, for example. |
The name of a map source which contains a list of mount points, and the file system location from which those mount points should be mounted. |
If supplied, these will apply to all entries in the given map provided they don't themselves have options specified. This behavior is different from autofs version 4 where options were cumulative. This has been changed to implement mixed environment compatibility. |
auto.misc file
Autofs Nfs Ubuntu
The general format of maps is similar to the master map, however the 'options' appear between the mount point and the location instead of at the end of the entry as in the master map:
mount-point [options] location
Description |
This refers to the autofs mount point. This can be a single directory name for an indirect mount or the full path of the mount point for direct mounts. Each direct and indirect map entry key (mount-point above) may be followed by a space separated list of offset directories (sub directory names each beginning with a '/') making them what is known as a multi-mount entry. |
Whenever supplied, these are the mount options for the map entries that do not specify their own options. |
This refers to the file system location such as a local file system path (preceded with the Sun map format escape character ':' for map names beginning with '/'), an NFS file system or other valid file system location. |
Enough with the explanation next edit auto.misc file
Save and exit the file
Description
Its time to reload our autofs services
Verify if autofs is running
Reloading maps
Make sure the NFS shares are not already mounted
So none of the NFS shares are mounted still lets try to access them
Notebook 4 0 6. Similarly you can try to access another share i.e. 'raid'
You can use the watch command to verify if the shares automatically gets unmounted.
After few seconds the mount point 'work' is automatically unmounted as you can see below
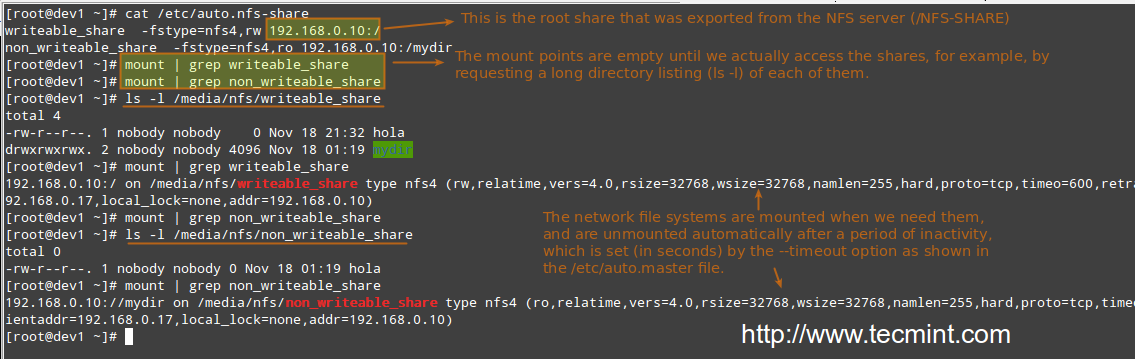
Notebook 4 0 6. Similarly you can try to access another share i.e. 'raid'
You can use the watch command to verify if the shares automatically gets unmounted.
After few seconds the mount point 'work' is automatically unmounted as you can see below
Autofs Nfs Example
Related Articles:

